What is a Shapefile?
A shapefile is a storage format for geographic data. Shapefiles can contain lines, points, polylines and polygons that represent different features on a map.
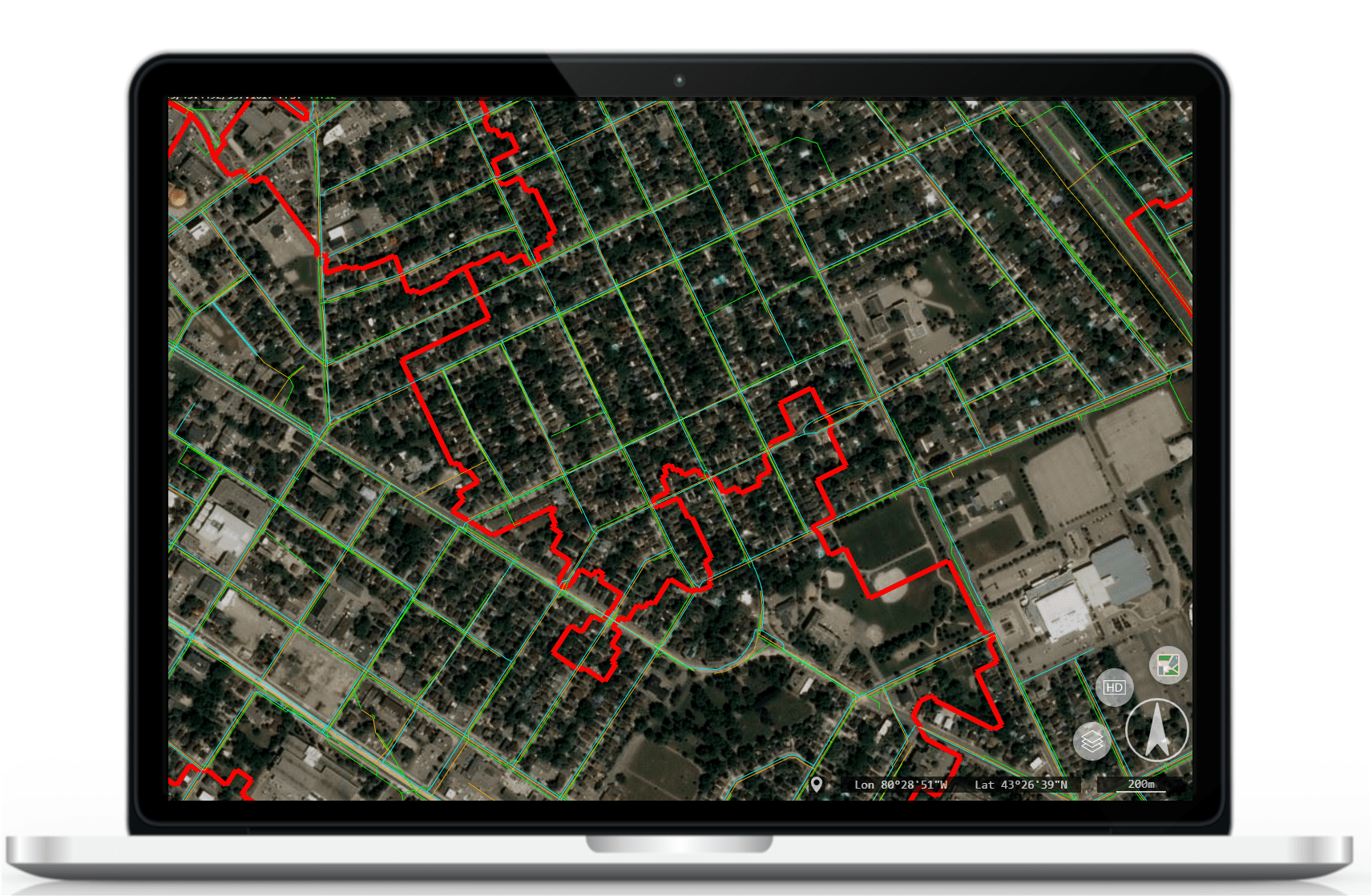
Each shapefile must contain at least three files – .shp, .shx, and .dbf. The .shp file contains the actual geometry data (e.g. points or lines). The .shx file contains a index to find the information (kind of like a reference for looking up data). The .dbf file contains attribute information (a table with more info about each feature). The image on the left shows two shapefile layers (green “storm sewers” and red “drainage areas”).
Shapefile Viewer
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software is typically required to open and view a shapefile. There are a few popular options that range from free to thousands of dollars per year. Equator is free and easy to use (no installation required), just click on “Go To Viewer” to give it a try. Other alternatives include ArcGIS, QGIS, or Google Earth.
Shapefile Library
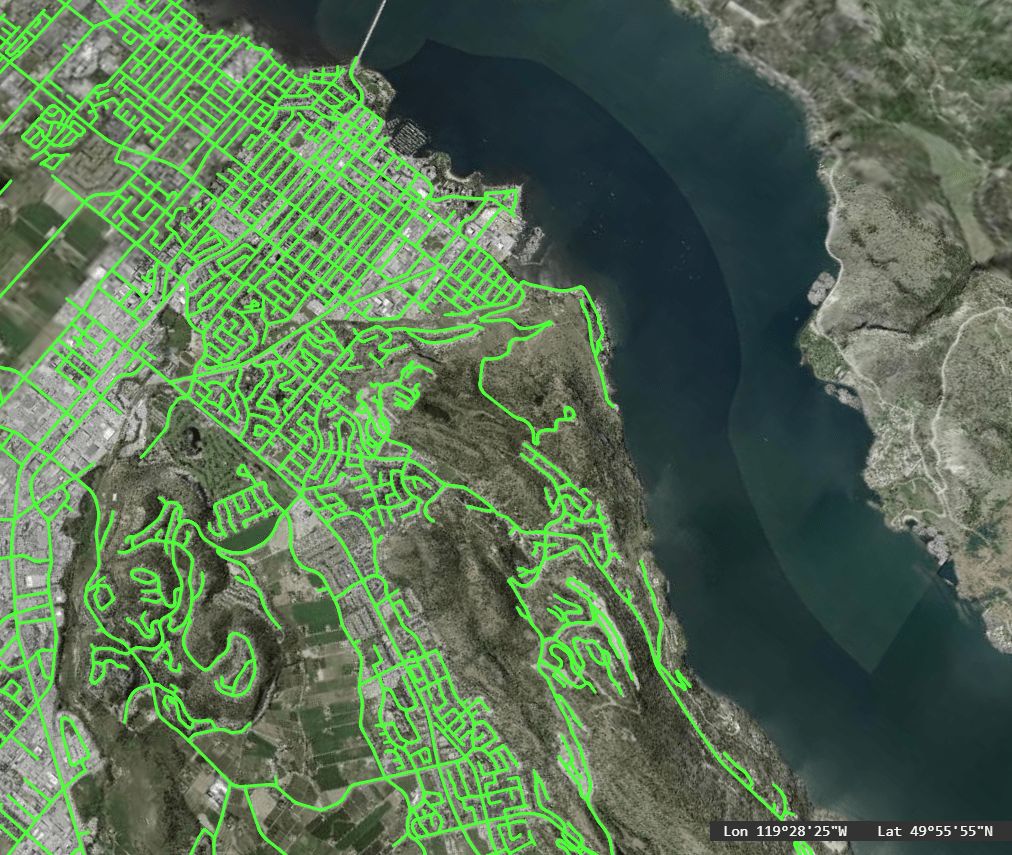
You can find thousands of shapefiles right in Equator. Source municipal data like roads, rivers, pipes, parks, buildings. You can also find spatial pattern data for your research such as climate & weather event, crime, historic sites and much more. Download shapefiles and create maps right within the Equator platform. Check out this tutorial to learn how, or click “Go To Viewer” to explore on your own.

Example Shapefile: Points
Each point marks a fire hydrant in the City of Bemidji, Minnesota, overlaid on Equator’s 3D terrain baselayer. There are 928 fire hydrants in Bemidji, as shown in the image on the left.
Shapefile Example: Polygons
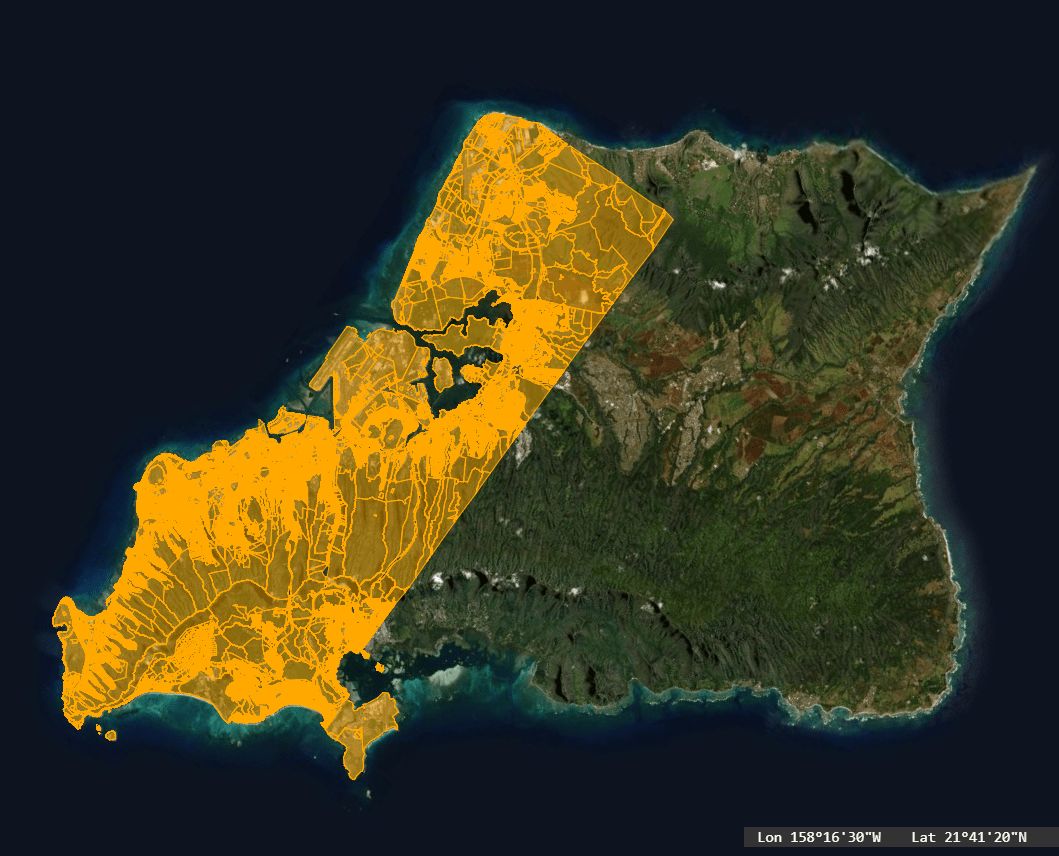
This polygon shapefile outlines the five boroughs of New York City (The Bronx, Brooklyn, Manhattan, Queens, and Staten Island). Queens is the largest borough with an area of 280KM². All attribute data for shapefiles can be viewed in a table when clicking on a feature in Equator.

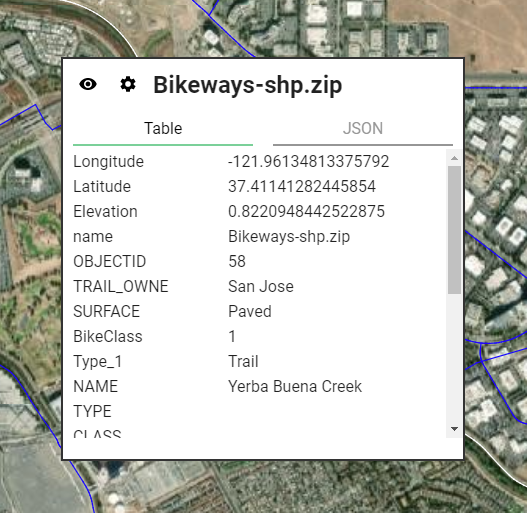
Shapefile Example: Lines
This line shapefile marks bikeways in San Jose, California, overlaid on Equator’s 3D terrain baselayer. Bikeways represented in this shapefile include lanes, trails and sharrows across the city.
The Attribute Table
The attribute table include details about a data set and specific features, created by the data provider. Typical information provided includes coordinates, name and ID. Many providers also choose to include ancillary data such as measurements, notes and any other classifications that may be relevant to the type of data.
The attributes for all data features within a shapefile can be viewed in a summary table within Equator. You can also select an individual feature to view it’s specific attributes.