Environmental Impact Assessments
EIAs: Your guide to responsible development

Did you know that the concept of environmental impact assessments (EIAs) dates back to the 1960s?
What is an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA)?
An environmental impact assessment (EIA) assesses the potential social, environmental, and economic impacts of a potential project. The purpose of an EIA is to ensure that decision makers consider the potential environmental consequences of their actions before deciding whether or not to proceed with a project. EIAs are typically required for large-scale projects that may have significant environmental impacts, such as construction of a new power plant or road, or extraction of natural resources. The specific requirements for conducting an EIA vary by country, but generally an EIA must be carried out before the project can be approved and implemented.

Photo of the Hercilium Luz Bridge under construction
How to perform an Environmental Impact Assessment
The steps taken to perform an environmental impact assessment (EIA) can vary depending on the specific requirements of the country in which the assessment is being conducted and the nature of the proposed project. However, there are some general steps that are typically followed in the EIA process:
Step 1: Screening
The first step in an EIA is to determine whether the proposed project requires an assessment. This is done through a screening process, which involves evaluating the potential impacts of the project and deciding whether an EIA is necessary.
Identify the proposed project
The first step in screening is to determine whether the proposed project requires an assessment. This is done through a screening process, which involves evaluating the potential impacts of the project and deciding whether an EIA is necessary.
Review relevant laws and regulations
The next step is to review the laws and regulations that apply to the proposed project, to determine whether an EIA is required. Different countries have different requirements for when an EIA is necessary, so it is important to understand the specific requirements of the country in which the project is being proposed.
Assess the potential impacts of the project
Once the proposed project has been identified and the relevant laws and regulations have been reviewed, the next step is to assess the potential environmental, social, and economic impacts of the project. This may involve gathering information about the project site, studying existing environmental conditions, and predicting how the project may affect those conditions.
Determine whether an EIA is necessary
Based on the information gathered during the first three steps, the decision maker can determine whether an EIA is necessary for the proposed project. If the potential impacts of the project are likely to be significant, an EIA will be required. If the potential impacts are not likely to be significant, an EIA may not be necessary.
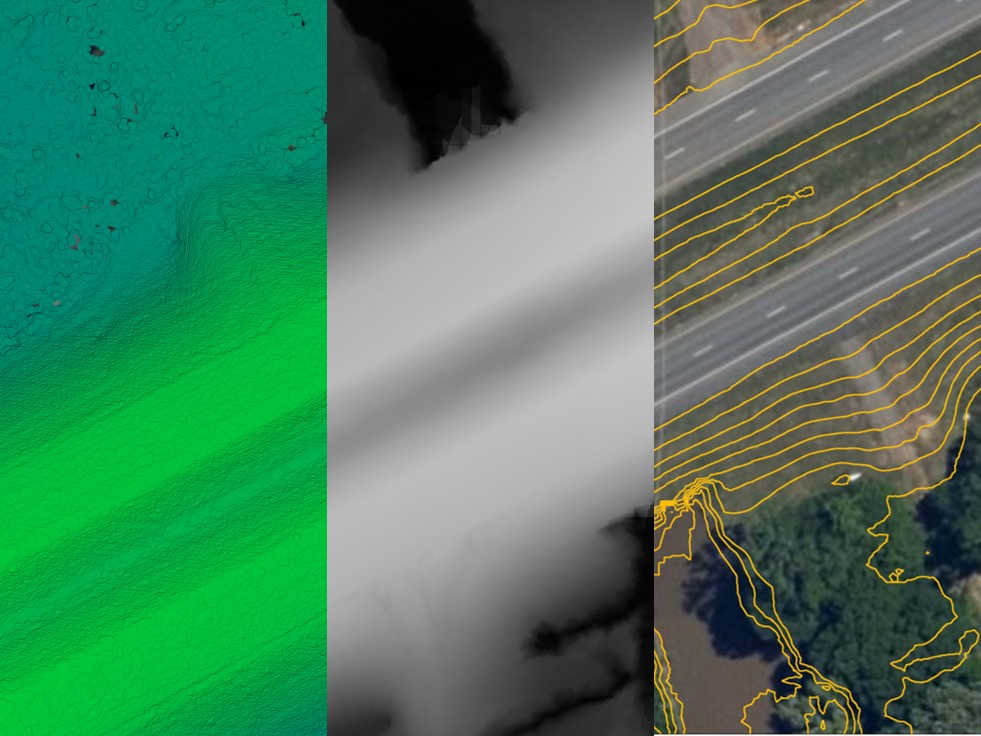
Did you know that environmental impact assessments (EIAs) are often conducted using specialized software, such as geographic information systems (GIS)? GIS allows users to create maps and spatial databases that can be used to analyze data about a project and its surrounding environment. For example, GIS can be used to create maps that show the location of a proposed project, the location of sensitive environmental resources (such as wetlands or wildlife habitats), and the potential impacts of the project on those resources. GIS can also be used to create 3D models that allow users to visualize the potential impacts of the project in more detail.
Step 2: Scoping
Scoping is the second step in the environmental impact assessment (EIA) process. The purpose of scoping is to define the scope of the assessment, which involves identifying the environmental, social, and economic impacts that need to be evaluated, as well as the methods and resources that will be used to gather and analyze information.
Identify the key issues
The first step in scoping is to identify the key issues that need to be addressed in the EIA. This may involve identifying the potential impacts of the project on different aspects of the environment (such as air quality, water resources, and wildlife habitats), as well as the potential social and economic impacts of the project.
Determine the level of detail required
The next step is to determine the level of detail that is required in the EIA. This may involve deciding which impacts need to be analyzed in more detail and which impacts can be analyzed more broadly.
Identify the appropriate methods and resources
Based on the key issues and the level of detail required, the next step is to identify the appropriate methods and resources that will be used to gather and analyze information. This may involve choosing specific data collection methods (such as field surveys or laboratory analyses), and deciding which experts or specialists will be consulted during the EIA process.
Step 3: Impact Analysis
The purpose of impact analysis is to evaluate the potential impacts of a proposed project on the environment, as well as on social and economic factors.
Collect data
The first step in impact analysis is to collect data about the project site, including information about the physical, biological, and social characteristics of the area. This may involve field surveys, laboratory analyses, and other data collection methods.
Assess existing conditions
The next step is to assess the existing conditions at the project site, including the quality of the air, water, and soil, as well as the presence of any sensitive environmental resources (such as wetlands or wildlife habitats).
Predict potential impacts
Based on the data collected and the assessment of existing conditions, the next step is to predict the potential impacts of the project on the environment and on social and economic factors. This may involve modeling the potential impacts of the project using computer software, or conducting a literature review to identify the potential impacts of similar projects.
Evaluate the significance of the impacts
The final step in impact analysis is to evaluate the significance of the potential impacts of the project. This may involve comparing the predicted impacts to relevant environmental standards or thresholds, or considering the views of stakeholders who may be affected by the project.
Did you know that the environmental impact assessment (EIA) process is designed to be transparent and participatory? One of the key principles of EIA is the involvement of relevant stakeholders in the assessment process. This may include local communities, government agencies, and environmental organizations, among others. Consultation with stakeholders is an important part of the EIA process, as it helps to ensure that the assessment considers the concerns and interests of these groups, and that the results of the assessment are communicated effectively. Stakeholder consultation also helps to increase the credibility and legitimacy of the EIA process, as it allows different perspectives to be considered and helps to build consensus around the assessment findings.
Step 4: Consultation with Relevant Stakeholders
Consultation with relevant stakeholders is the fourth step in the environmental impact assessment (EIA) process. The purpose of stakeholder consultation is to ensure that the EIA considers the concerns and interests of groups that may be affected by the proposed project, and to ensure that the results of the EIA are communicated effectively.
Identify the stakeholders
The first step is to identify the groups that may be affected by the proposed project, or who have an interest in the project. This may include local communities, government agencies, environmental organizations, and other groups.
Determine the appropriate methods of consultation
The next step is to determine the most appropriate methods of consultation for each stakeholder group. This may involve holding public meetings, conducting surveys or focus groups, or providing information through newsletters or other means.
Consult with stakeholders
Once the appropriate methods of consultation have been determined, the next step is to engage in consultation with the identified stakeholder groups. This may involve presenting information about the project and the EIA process, answering questions, and soliciting feedback from stakeholders.
Document the consultation process
It is important to document the consultation process, including the methods used, the stakeholders consulted, and the feedback received. This documentation can be used to demonstrate that the EIA process was transparent and participatory, and to inform the final assessment report.
Step 5: Mitigation and Monitoring
The purpose of mitigation and monitoring is to minimize any negative impacts of the proposed project on the environment, and to ensure that the project is implemented in a sustainable manner.
Identify the potential impacts
We have already predicted potential impacts, but now it is time to identify the actual potential impacts of the project that need to be addressed. This may include impacts on air quality, water resources, wildlife habitats, and other environmental factors.
Develop a mitigation plan
Based on the identified impacts, the next step is to develop a plan for mitigating those impacts. This may involve implementing measures to reduce pollution, protect wildlife, or minimize other negative impacts of the project.
Implement the mitigation plan
Once the mitigation plan has been developed, the next step is to implement the measures outlined in the plan. This may involve installing pollution control equipment, establishing wildlife habitat protection areas, or implementing other measures to reduce the impacts of the project.
Monitor the impacts of the project
The final step in the mitigation and monitoring process is to establish a system for monitoring the impacts of the project over time. This may involve collecting data on the environmental, social, and economic impacts of the project, and using that data to assess the effectiveness of the mitigation measures. If the monitoring data indicates that the mitigation measures are not sufficient to address the impacts of the project, additional measures may need to be implemented.
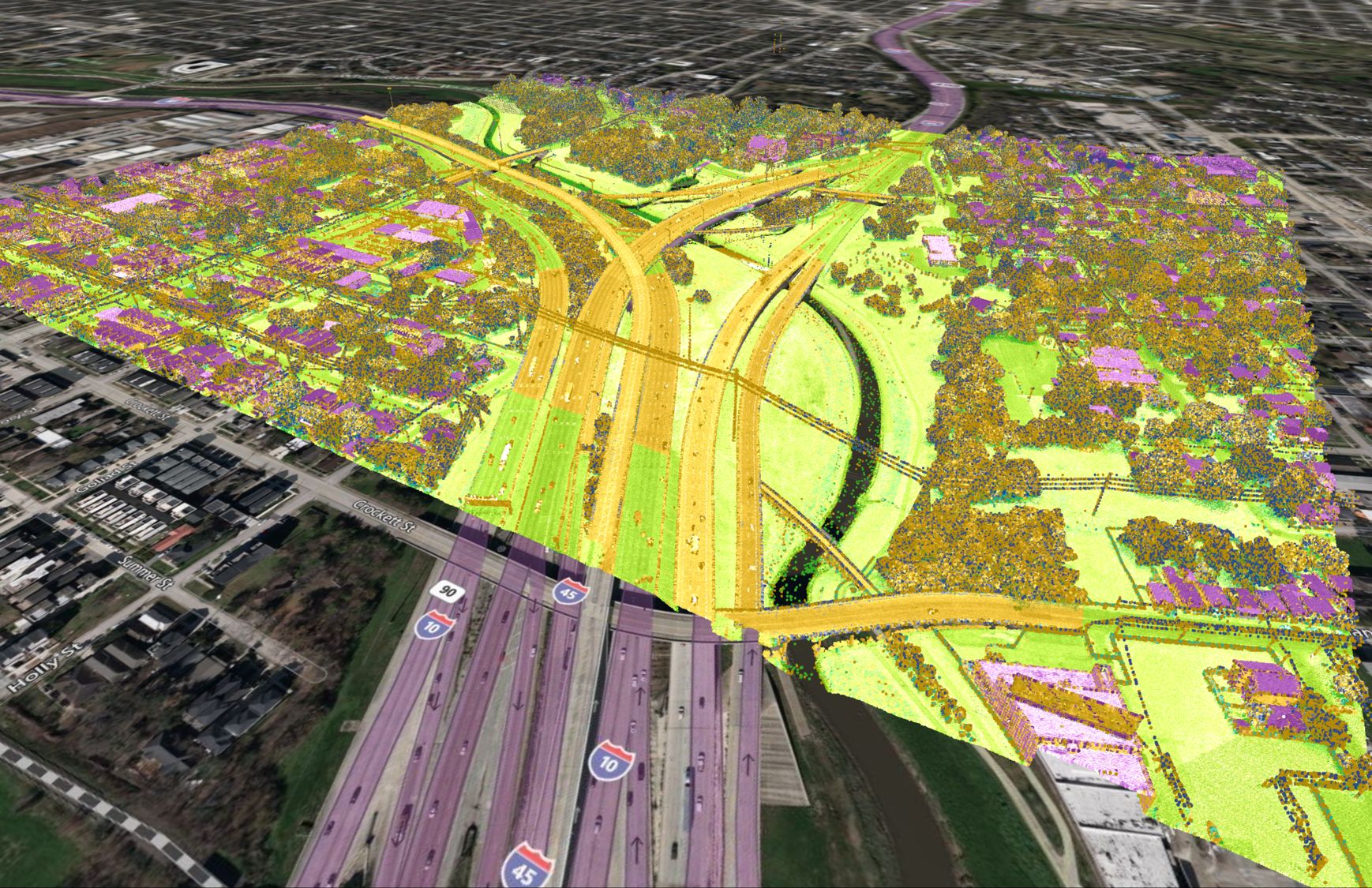
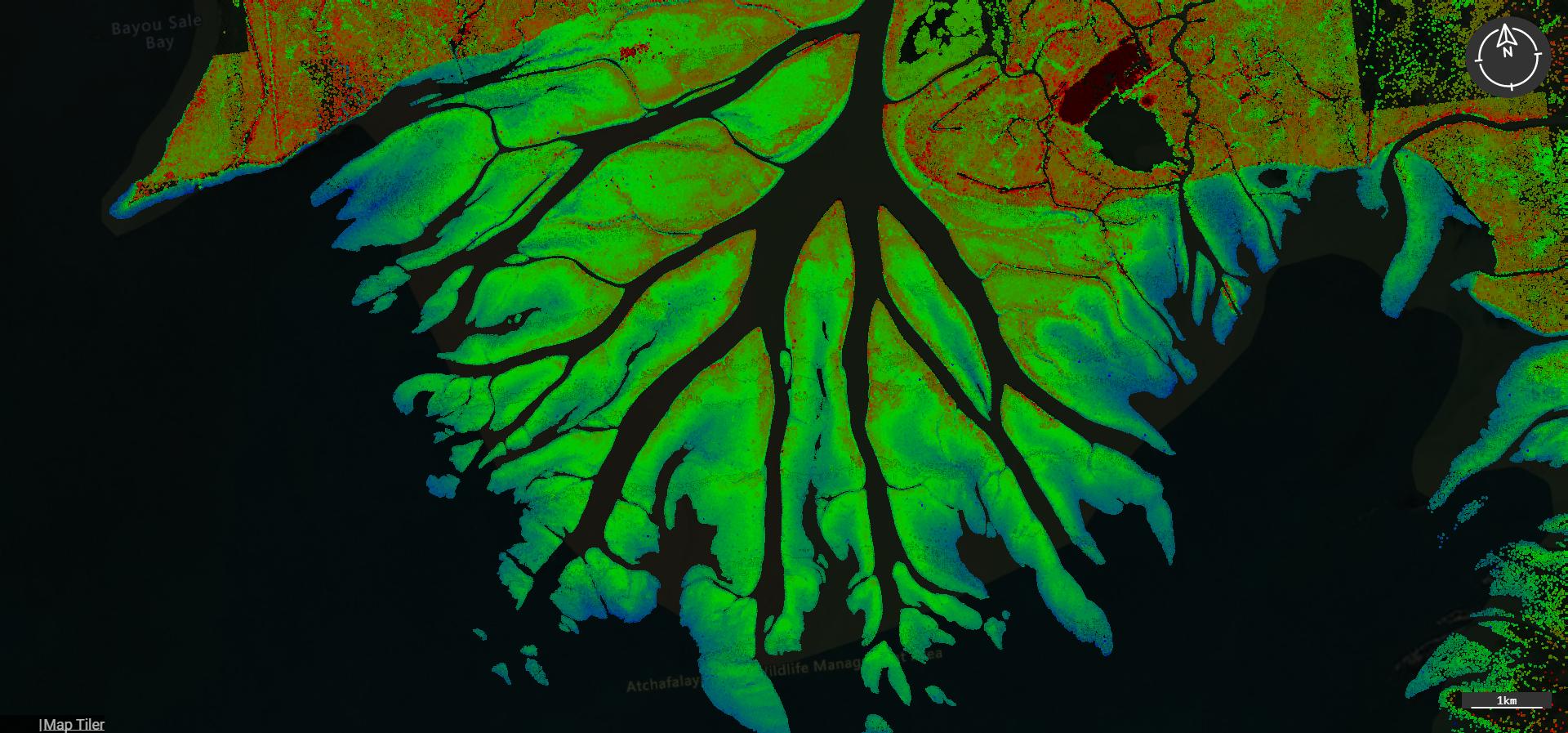
The Importance of GIS in Environmental Impact Assessments
Geographic information systems (GIS) are frequently used in environmental impact assessments (EIAs) to help analyze and visualize the potential impacts of a proposed project. GIS allows users to create maps and spatial databases that can be used to analyze data about a project and its surrounding environment. For example, GIS can be used to create maps that show the location of a proposed project, the location of sensitive environmental resources (such as wetlands or wildlife habitats), and the potential impacts of the project on those resources. GIS can also be used to create 3D models that allow users to visualize the potential impacts of the project in more detail.

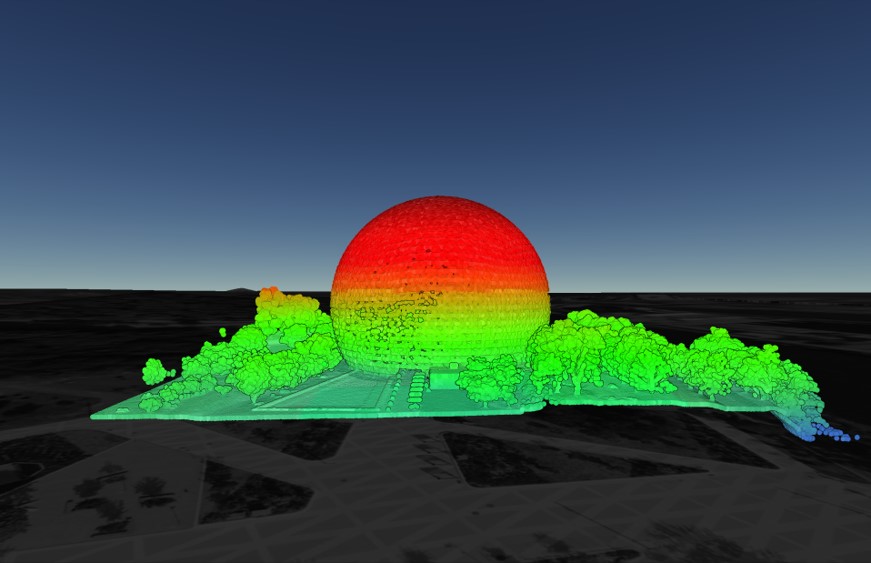
LiDAR pointcloud generated in Equator
The Future of Environmental Impact Assessments: Innovations and Challenges
As the world continues to focus increasingly on climate change and environmental degradation, the requirement for environmental impact assessments (EIAs) is only set to increase.
One challenge is the need to incorporate new technologies and approaches into the EIA process. For example, the use of geographic information systems (GIS) and other spatial analysis tools has become increasingly common in EIAs, as they allow users to create detailed maps and models of the potential impacts of a project. However, the adoption of these technologies also brings its own set of challenges, including the need to ensure that they are widely adopted and used appropriately and ethically. The deployment of new energy technologies (such as offshore wind farms) may require EIAs to consider the impacts on marine ecosystems, for example.
As economic globalization continues to increase, EIAs may also need to consider the impacts of global supply chains and the movement of goods and resources across national borders. At the same time, as the global population continues to grow, EIAs may need to begin to consider the impacts of increased demand for resources (such as land, water, and energy).