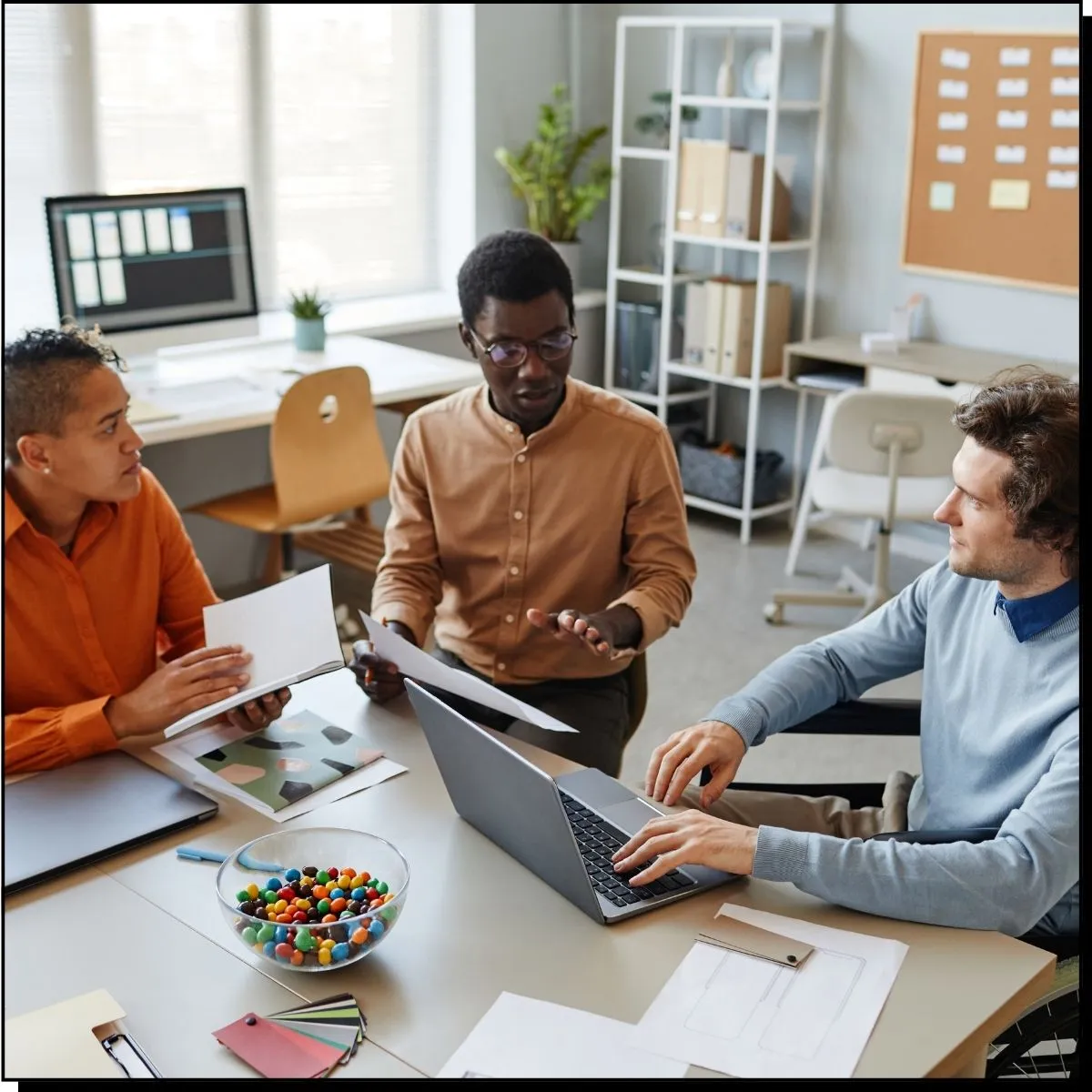
What software do I need to create a GIS?
There are many different software options available for creating a GIS. Some of the most popular software programs include:
Esri ArcGIS: This is a suite of GIS software products that are widely used in the public and private sectors. It includes tools for mapping, analysis, data management, and visualization.
QGIS: This is an open-source GIS software program that is available for free. It has many of the same features as ArcGIS, but is often used by smaller organizations or individuals who do not have the budget for a commercial GIS software program.
AutoCAD Map: This is a GIS software program that is part of the AutoCAD suite of design and drafting tools. It is often used by engineers, surveyors, and other professionals who need to create detailed maps and spatial data.
Equator: When working with GIS software you need files to work with. Equator allows you to get the files you need to create a GIS.
There are many other GIS software programs available, and the right one for you will depend on your specific needs and budget.
Why is GIS Valuable?
GIS is a valuable tool because it allows users to analyze and visualize data in a spatial context, which can provide insights and understanding that may not be apparent from tabular data alone. For example, GIS can be used to identify patterns and trends in data that are geographically distributed, such as the distribution of diseases in a population or the location of natural resources.
GIS can also be used to create maps and other visualizations that can be used to communicate information to a wide audience. In this way, GIS can be a powerful tool for decision-making and problem-solving.
GIS can also be used to support the management of resources and infrastructure, such as water, energy, transportation, and land use. By capturing and analyzing data about these resources, GIS can help organizations make more informed decisions about how to allocate resources and plan for the future.
Overall, GIS has the potential to provide valuable insights and support decision-making in a wide range of fields and applications.
What Is Geo-coding?
Geo-coding is the process of assigning geographic coordinates (such as latitude and longitude) to a location or address. This can be done using a GIS or other mapping software. Geo-coding is often used to plot locations on a map or to analyze patterns and trends in data that are geographically distributed.
What are the major GIS functions?
Some of the main processes that can be applied to vector data in a GIS include:
Buffering: This process creates a zone around a vector feature, such as a point, line, or polygon, and is often used to create a spatial context for analysis or to identify features that are within a certain distance of a given feature.
Clipping: This process extracts a portion of a vector dataset based on a specified boundary or area of interest.
Overlay: This process combines two or more vector datasets in order to create a new dataset that contains features from both datasets.
Dissolve: This process combines adjacent polygons that share a common attribute into a single polygon.
Intersection: This process identifies the spatial intersection of two vector datasets, such as the points where two roads intersect or the area where two land use categories overlap.
Union: This process combines the features of two vector datasets into a single dataset.
These processes can be used to manipulate vector data and to identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
What are the main components of a GIS?
The main components of a GIS include:
Hardware: This includes the computer equipment and other physical components that are used to run the GIS.
Software: This is the program or programs that are used to create, manage, and analyze spatial data.
Data: This includes the spatial data and associated attributes that are stored, managed, and analyzed by the GIS.
People: This includes the individuals who use the GIS, such as GIS analysts, cartographers, and other professionals.
What is the difference between GIS commands and GIS tools?
GIS commands are instructions that are entered into the GIS software to perform a specific task. These commands are typically entered into a command line or a command prompt.
GIS tools, on the other hand, are graphical user interface (GUI) elements that can be clicked or selected in order to perform a specific task. These tools may include buttons, menus, and other elements that allow users to interact with the GIS software.
What is the digitizing process?
Digitizing is the process of converting paper maps or other analog data into a digital format that can be used in a GIS. This typically involves using a digitizing tablet or other input device to trace over the features on the map and capture their locations and other attributes. The resulting digital data can then be imported into a GIS and used for mapping, analysis, and other tasks.
How are vectors connected to other lines?
In a GIS, vectors are often connected to other lines in order to create a network. For example, a vector representing a road might be connected to other vectors representing other roads, intersections, and other features. These connections can be used to represent the spatial relationships between different features and to analyze the flow of resources or information through the network.
What is GIS metadata?
GIS metadata is data that describes the characteristics and content of spatial data. Some examples of GIS metadata include:
- Map title
- Map scale
- Coordinate system
- Data source
- Data creation date
- Data update frequency
- Data accuracy
GIS metadata is important because it helps users understand the context and limitations of the spatial data.
What is a thematic raster dataset?
A thematic raster dataset is a type of spatial data that represents a particular theme or attribute. It is typically composed of pixels, with each pixel representing a specific attribute or value. Thematic raster datasets are often used to represent data such as elevation, land cover, or population density.
What is a point feature?
In a GIS, a point feature is a spatial feature that is represented by a single point. Point features can be used to represent a wide variety of features, such as buildings, trees, wells, and other features that can be accurately represented as a single point.
What is a polygon feature?
In a GIS, a polygon feature is a spatial feature that is represented by a closed loop of lines. Polygon features are often used to represent areas, such as parcels of land, bodies of water, or other features that can be accurately represented as a closed loop.
What are the main processes that can be applied on vector data?
Some of the main processes that can be applied to vector data in a GIS include:
Buffering: This process creates a zone around a vector feature, such as a point, line, or polygon, and is often used to create a spatial context for analysis or to identify features that are within a certain distance of a given feature.
Clipping: This process extracts a portion of a vector dataset based on a specified boundary or area of interest.
Overlay: This process combines two or more vector datasets in order to create a new dataset that contains features from both datasets.
Dissolve: This process combines adjacent polygons that share a common attribute into a single polygon.
Intersection: This process identifies the spatial intersection of two vector datasets, such as the points where two roads intersect or the area where two land use categories overlap.
Union: This process combines the features of two vector datasets into a single dataset.
These processes can be used to manipulate vector data and to identify patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
Is GIS a growing industry?
GIS is a growing industry, with the demand for GIS professionals expected to increase in the coming years. The use of GIS is increasing in many fields, including environmental management, urban planning, transportation, and natural resource management, among others. As the use of GIS continues to expand, the demand for skilled professionals in this field is likely to grow.
How many years of education do I need to get into a GIS career path?
The educational requirements for a GIS career path can vary depending on the specific job and the employer’s requirements. Some entry-level positions may only require a two-year associate’s degree in GIS or a related field, while more advanced positions may require a four-year bachelor’s degree or higher.
In general, a bachelor’s degree in GIS or a related field, such as geography, computer science, or engineering, is a good foundation for a career in GIS. Many universities offer GIS-specific programs or GIS coursework as part of a broader degree program.
What type of data types do GIS professionals work with?
GIS professionals typically work with two main types of data: vector data and raster data. Vector data is composed of points, lines, and polygons that represent spatial features, while raster data is composed of cells or pixels that represent a continuous surface or attribute. GIS professionals may work with one or both of these data types, depending on the specific needs of their project.
GIS professionals may also work with other types of data, such as tabular data, which is data that is organized into rows and columns, and text data, which is data that is stored as plain text. GIS professionals may also work with data from a variety of sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photography, field surveys, and other sources.