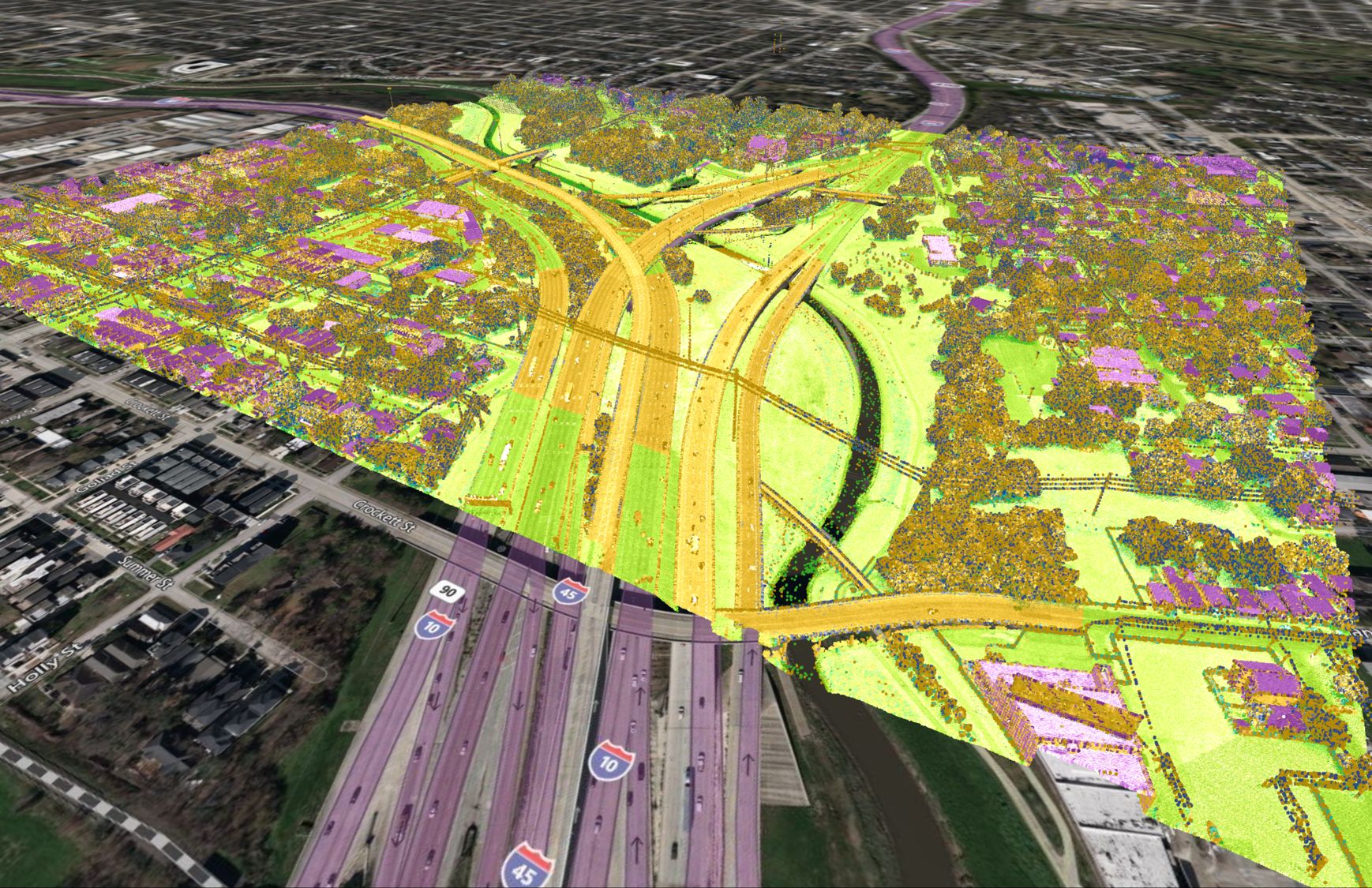
GIS for Transportation
Introduction
GIS, or geographic information systems, is a powerful tool that is increasingly being used in the transportation sector. GIS enables the analysis and visualization of spatial data, allowing for the integration of geographical elements into transportation planning and management. The benefits of using GIS in transportation are numerous, including improved efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Examples of how GIS is used in transportation
GIS is used in a variety of transportation applications. One common use is route planning and analysis, where GIS can be used to identify the most efficient or cost-effective routes for vehicles. GIS can also be used for traffic analysis and management, such as by analyzing traffic patterns and identifying bottlenecks or areas of congestion. Public transportation planning and scheduling is another area where GIS can be useful, as it can help to optimize routes and schedules based on demand and other factors. Fleet management and logistics is another area where GIS can be applied, allowing for the tracking and optimization of vehicle routes and resources.
Case studies of GIS in transportation
One example of GIS being used in transportation is the implementation of a GIS-based transportation management system by a city. For instance, a city may use GIS to analyze traffic patterns and identify areas where traffic flow could be improved. This could involve using GIS to analyze data on traffic volume, accidents, speed, and other factors to identify problem areas. Based on this analysis, the city could then implement measures such as adjusting signal timing or adding turn lanes to improve traffic flow. The results of using GIS in this way could include reduced congestion, shorter travel times, and improved safety.
Challenges and considerations when using GIS in transportation
There are several challenges and considerations to keep in mind when using GIS in transportation. One issue is data quality and availability. Accurate and up-to-date data is essential for GIS to be effective, but this can be difficult to obtain in some cases. Another challenge is the integration of GIS with other systems and technologies. GIS is often used in conjunction with other tools, such as transportation modeling software, and ensuring smooth integration can be a challenge. Additionally, implementing and maintaining a GIS system can require significant resources, including both financial and human resources.
Future of GIS in transportation
The future of GIS in transportation is bright, with emerging trends and technologies offering even more potential for its use. One such trend is the development of autonomous vehicles, which will require sophisticated GIS systems to navigate and operate safely. The integration of GIS with artificial intelligence is another area of potential growth, as AI can help to analyze and interpret large amounts of data in real-time. These and other innovations have the potential to further revolutionize transportation planning and management, making it more efficient, safe, and sustainable.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GIS is an essential tool for transportation planning and management, offering a wide range of benefits and applications. As transportation continues to evolve, GIS will play a crucial role in enabling the efficient and sustainable movement of people and goods.